- What We Do
- Agriculture and Food Security
- Democracy, Human Rights and Governance
- Economic Growth and Trade
- Education
- Ending Extreme Poverty
- Environment and Global Climate Change
- Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment
- Global Health
- Water and Sanitation
- Working in Crises and Conflict
- U.S. Global Development Lab
The last 50 years have seen a historic five-fold increase in gross domestic product per capita in the world, driven by demographic changes, global trade and better governance, with half of low-income countries graduating to higher income status since the year 2000. In addition to providing direct funding for health, The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) works with country governments to increase domestic financing for this sector.
Development Financing Is Undergoing a Transformation
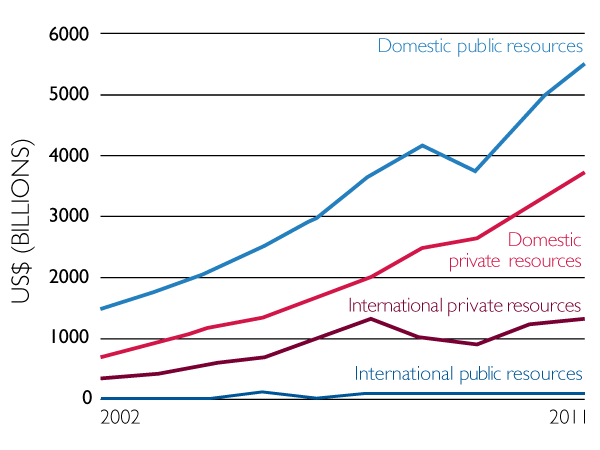
- Financing for development has grown rapidly in the 21st century from both public and private sources to and within developing countries.
- Domestic resources account for the largest source of development financing through growth in GDP, tax revenue and local private capital.
- Private resources, whether from domestic markets or international investment, play an important role in financing development.
- Donor financing and international public resources are making up a smaller share of development financing.
USAID’s Development Credit Authority Mobilizes Resources for Health.
USAID uses many tools to leverage global health financing and increase healthcare access where it’s desperately needed. The Development Credit Authority is one of those tools that works with USAID Missions and local banks to mobilize financing for private clinics around the world.







Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.