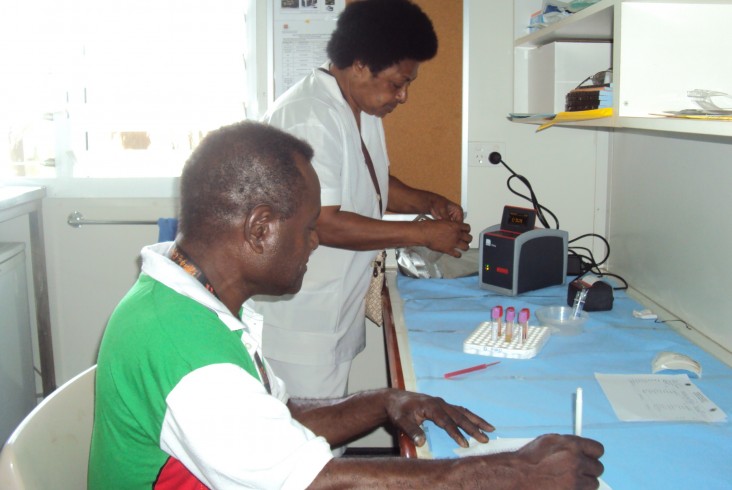
USAID supplied three CD4 machines to clinics that provide antiretroviral therapy services. Pictured here is the Id Inad Clinic in Madang, Papua New Guinea, where 112 HIV positive patients now have the opportunity to receive regular monitoring.
Elaine Galore, FHI 360
Papua New Guinea suffers from the highest rate of HIV/AIDS in the Pacific, with overall adult prevalence at nearly one percent. Current data points to a more concentrated HIV epidemic linked to high risk populations, such as female sex workers and their clients, and men who have sex with men.
A 2010 study conducted by the PNG Institute of Medical Research revealed these statistics:
- 19% HIV prevalence for women who exchange sex
- 8.8% for men who exchange sex
- 23.7% for transgender persons who exchange sex and
- 9% for for men who have sex with men
USAID program data indicates that HIV was detected in:
- 12.2 % of women in transactional sex
- 11.9 % of high-risk women
- 4.7 % of men in transactional sex
- 8.0 % of high-risk men
- 2.8 % of men who have sex with men and transgender people
ACTIVITIES
- USAID - in collaboration with local and national governments, and civil society partners - is addressing this mounting public health concern by improving the country’s ability to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. This includes strengthening the overall health system, which allows for successful HIV efforts to be replicated. USAID also works in cross-cutting issues such as sexually transmitted infections, tuberculosis, gender based violence, and training of health workers.
-
USAID developed the Continuum of Prevention to Care and Treatment mode, which is now applied worldwide at other USAID Missions. It assists civil society and government partners to implement, sustain and replicate it in their respective regions. Key components of the model include:
- Case management
- Community outreach
- Referrals
- Quality care and treatment in health facilities, HIV testing & counseling and GBV services.
- USAID assists local partners to collect data, manage supplies, and oversee their programs. At the national level, USAID actively participates in technical working groups to ensure a coordinated, effective HIV response.
- USAID is strengthening and expanding HIV/AIDS services in the National Capital District and Madang Province. USAID links prevention, care, support, and treatment services for people vulnerable to, living with and affected by HIV/AIDS and also aims to increase demand for services by key populations, their sexual partners, and their families. Services are provided in homes, communities, and in health facilities.
In May 2013, the Government of Papua New Guinea’s midterm review of the National HIV/AIDS Strategy cited the USAID’s Continuum of Prevention to Care and Treatment model as a high impact HIV strategy and called for the model’s replication nationally.







Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.