
Overview
To achieve long-term stability and economic growth, Haiti must establish representative and accountable governance institutions as well as ensure access to justice. While many of Haiti’s governance challenges pre-date the 2010 earthquake, that catastrophe further highlighted the need for an increased focus on governance and government accountability.
Haiti has experienced a series of political set-backs in recent history that continue to detract from efforts to improve governance institutions and enforceable legal norms. Although the country has the formal structures of a democracy, many of these have yet to become fully functional, as evidenced by recurring periods of political and institutional instability. Haiti’s state institutions are under-resourced, and provide limited services to only a small percentage of the population. Despite these challenges, some progress has been made in recent years to advance the functioning of national and local government, civic engagement, voter education, access to justice services, and protection of human rights.
USAID Strategy and Activities
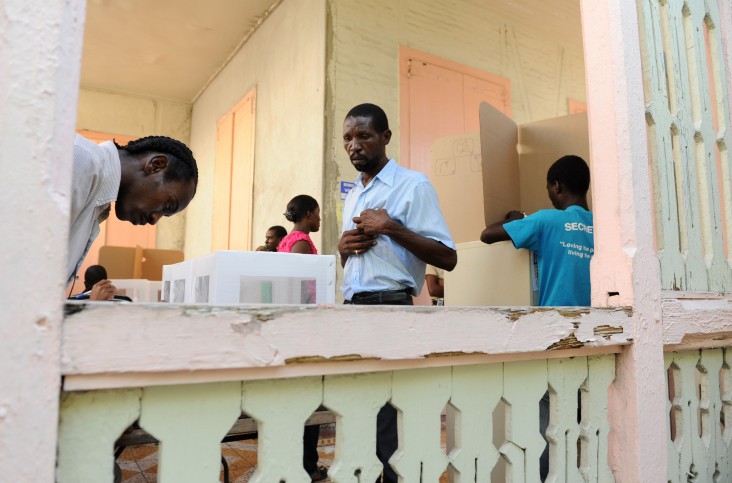
Supporting Credible Political and Electoral Processes
-
Building the capacity of haitian electoral authorities to conduct elections.
-
Strengthening the capacity of election observers – domestic and international – to provide credible and impartial assessments of election processes.
-
Increasing civic and voter education as well as ensuring that women and persons with disabilities can fully participate in the electoral process.
-
Training women candidates to improve their campaigning and political participation skills.
Strenghtening National and Local Governance
-
Promoting transparency and government accountability through an Integrated Financial Management System, which provides automated financial functions, enhanced control of revenues and expenditures, and facilitation of investigations. This program is also facilitating exchange of high volumes of data efficiently and securely between 13 government institutions through the Unified Data Exchange Platform.
-
Supporting decentralization by building the capacity of nine targeted municipal governments to more effectively and transparently plan, collect, and manage revenues, deliver basic services, and coordinate emergency relief efforts.
-
Modernizing civil service by improving government human resource management, including introducing competitive hiring in the public sector through a partnership between USAID and the Haitian government’s Office of Management and Human Resource.
Improving Access to Justice and Legal Assistance
-
Addressing pretrial detention through the provision of equipment, technical assistance, and improved case management in targeted jurisdictions. USAID deployed Haiti’s first computerized case management information system in Fort-Liberté, Saint-Marc, and Port-au-Prince.
-
Providing legal assistance to underserved residents of Port-au-Prince, Saint-Marc, Croix des Bouquets, Cap-Haïtien, and Fort Liberté.
-
Assisting the High Judicial Council to provide independent oversight of the judiciary, including to the Judicial Inspection Unit and the vetting committee for judges.
-
Supporting the reform of the Penal Code and Criminal Procedure Code through assistance to the Ministry of Justice’s Criminal Code Reform Commission.
Protecting Human Rights and Vulnerable Populations
-
Addressing gender-based violence through advocacy on improved legislation and services for survivors.
-
Combatting trafficking-in-persons through support for implementation of legislation, the inter-ministerial commission, and monitoring prosecutions.
-
Assisting at-risk, institutionalized children as well as children in domesticity (“restaveks”) through the strengthening of child welfare and protection systems.
- Reducing discrimination against vulnerable populations by supporting awareness raising and advocacy.







Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.