- What We Do
- Agriculture and Food Security
- Democracy, Human Rights and Governance
- Economic Growth and Trade
- Education
- Ending Extreme Poverty
- Environment and Global Climate Change
- Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment
- Global Health
- Water and Sanitation
- Working in Crises and Conflict
- Disaster Assistance
- Political Transition Initiatives
- Conflict Mitigation and Prevention
- Countering Violent Extremism
- Disaster Risk Reduction
- Peacebuilding and Reconciliation
- Providing Safe & Secure Environments for Development
- Recovering From Crisis
- Resilience
- Tech Challenge for Atrocity Prevention
- World Humanitarian Day
- U.S. Global Development Lab

Latest Yemen Fact Sheet
Yemen Complex Emergency Fact Sheet #16 - 09-22-2017 ![]() (pdf - 224k)
(pdf - 224k)
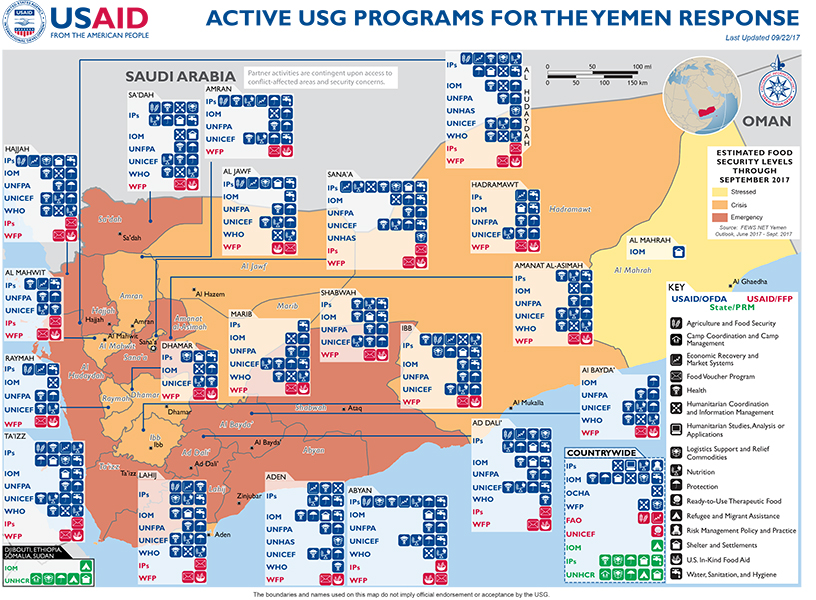
Yemen Map - 09-22-2017 ![]() (pdf - 771k)
(pdf - 771k)
view text version [pdf, 224kb]
Yemen Arabic Fact Sheet #16 - 09-22-2017 ![]() (pdf - 545k)
(pdf - 545k)
Key Developments
On September 21, USAID Administrator Mark Green announced approximately $575 million in new humanitarian funding to support emergency response activities in Nigeria, Somalia, South Sudan, and Yemen—the four conflict-affected countries facing severe food insecurity and malnutrition crises—as well as neighboring countries hosting refugees fleeing those crises. The new funding for Yemen includes approximately $112.7 million from USAID’s Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance (USAID/OFDA) and $55.8 million from USAID’s Office of Food for Peace, bringing total U.S. government (USG) humanitarian assistance in Yemen to nearly $636 million to date in FY 2017. UN agencies and non-governmental organizations plan to use the new assistance to address Yemen’s food security crisis and unprecedented cholera outbreak.
As of September 19, health agencies had recorded nearly 700,000 suspected cholera cases and 2,101 related deaths since the outbreak resurged in late April, according to USAID/OFDA partner the UN World Health Organization. USG partners are distributing cholera prevention supplies, such as water purification tablets; establishing additional cholera treatment centers and oral rehydration centers; and providing safe drinking water to vulnerable populations.
Access constraints continue to hinder humanitarian response activities in Yemen. Approximately 700,000 people in acute need of relief assistance live in districts where humanitarian access is highly constrained, according to the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs.
HUMANITARIAN FUNDING TO YEMEN IN FY 2017*
|
USAID/OFDA |
$227,996,106 |
|
USAID/FFP |
$369,629,239 |
|
State/PRM |
$38,125,000 |
|
Total U.S. Government Assistance to Yemen and Neighboring Countries |
$635,750,345 |
*These figures are current as of September 22, 2017
Background
Between 2004 and early 2015, conflict between the Republic of Yemen Government (RoYG) and Al Houthi opposition forces in the north and between Al Qaeda-affiliated groups and RoYG forces in the south, forced people in northern Yemen to repeatedly flee their homes, resulting in the need for humanitarian aid. At the same time, fighting between RoYG forces and tribal and militant groups since 2011 limited the capacity of the RoYG to provide basic services, and humanitarian needs increased among impoverished populations. In late March 2015, a coalition led by the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia began airstrikes on Al Houthi and allied forces to halt their southward expansion. The ongoing conflict has damaged public infrastructure, interrupted essential services, displaced populations, and reduced the level of commercial imports to a fraction of the levels required to sustain the Yemeni population. The country relies on imports for 90 percent of its grain and other food sources. The escalated conflict, coupled with protracted political instability, the resulting economic crisis, rising fuel and food prices, and high unemployment, has left nearly 19 million people in need of humanitarian aid, and has put more than 17 million people at risk of starvation.










Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.