- What We Do
- Agriculture and Food Security
- Democracy, Human Rights and Governance
- Economic Growth and Trade
- Education
- Ending Extreme Poverty
- Environment and Global Climate Change
- Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment
- Global Health
- Water and Sanitation
- Working in Crises and Conflict
- Disaster Assistance
- Political Transition Initiatives
- Conflict Mitigation and Prevention
- Countering Violent Extremism
- Disaster Risk Reduction
- Peacebuilding and Reconciliation
- Providing Safe & Secure Environments for Development
- Recovering From Crisis
- Resilience
- Tech Challenge for Atrocity Prevention
- World Humanitarian Day
- U.S. Global Development Lab

Latest Sudan Fact Sheet
Sudan Complex Emergency Fact Sheet #5 - 07-27-2017 ![]() (pdf - 189k)
(pdf - 189k)
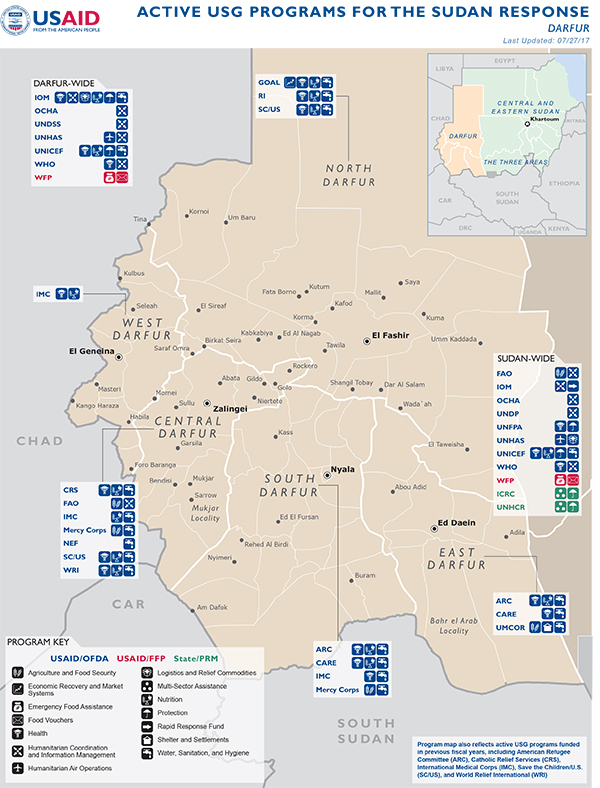
Sudan Map - 07-27-2017 ![]() (pdf - 750k)
(pdf - 750k)
view text version [pdf, 189kb]
Key Developments
Improved humanitarian access in Jebel Marra—a mountainous region that encompasses parts of Central Darfur, North Darfur, and South Darfur states—in recent months has enabled relief actors to identify critical humanitarian needs, including concerning levels of acute malnutrition and child mortality.
As of July 7, health actors had recorded more than 23,200 cases of acute watery diarrhea since August 2016, according to the UN World Health Organization and the Government of Sudan Ministry of Health.
Since late May, USAID has provided nearly $35 million in additional humanitarian assistance—including nearly $20 million from USAID’s Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance and $15 million from USAID’s Office of Food for Peace—for the Sudan response, bringing total U.S. government humanitarian assistance in FY 2017 to more than $175 million.
Background
Sudan continues to cope with the effects of conflict, economic shocks, and recurrent environmental hazards, such as drought and flooding, resulting in 4.8 million in need of humanitarian assistance. This includes 2.1 million internally displaced persons (IDPs) in Darfur, 230,000 IDPs in the government controlled parts of the Two Areas of South Kordofan and Blue Nile states, and 545,000 IDPs residing in locations in the Two Areas that are not under government control. USAID/OFDA is addressing the acute and protracted needs of conflict-affected populations in Sudan by prioritizing integrated activities in health, nutrition, and water, sanitation, and hygiene. The United States has declared has declared a disaster in Sudan each year since 1987 due to the ongoing complex emergency. As the largest international donor of humanitarian assistance in Sudan, the United States continues to provide impartial, needs-based assistance to vulnerable and conflict-affected populations.









Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.