- What We Do
- Agriculture and Food Security
- Democracy, Human Rights and Governance
- Economic Growth and Trade
- Education
- Ending Extreme Poverty
- Environment and Global Climate Change
- Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment
- Global Health
- Water and Sanitation
- Working in Crises and Conflict
- Disaster Assistance
- Political Transition Initiatives
- Conflict Mitigation and Prevention
- Countering Violent Extremism
- Disaster Risk Reduction
- Peacebuilding and Reconciliation
- Providing Safe & Secure Environments for Development
- Recovering From Crisis
- Resilience
- Tech Challenge for Atrocity Prevention
- World Humanitarian Day
- U.S. Global Development Lab
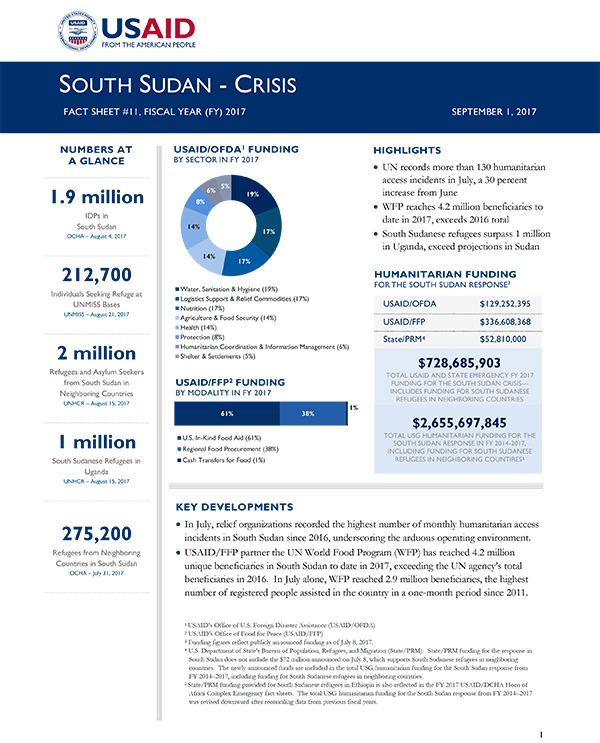
September 01, 2017
Highlights
- UN records more than 130 humanitarian access incidents in July, a 30 percent increase from June
- WFP reaches 4.2 million beneficiaries to date in 2017, exceeds 2016 total
- South Sudanese refugees surpass 1 million in Uganda, exceed projections in Sudan
Key Developments
In July, relief organizations recorded the highest number of monthly humanitarian access incidents in South Sudan since 2016, underscoring the arduous operating environment.
USAID/FFP partner the UN World Food Program (WFP) has reached 4.2 million unique beneficiaries in South Sudan to date in 2017, exceeding the UN agency’s total beneficiaries in 2016. In July alone, WFP reached 2.9 million beneficiaries, the highest number of registered people assisted in the country in a one-month period since 2011.
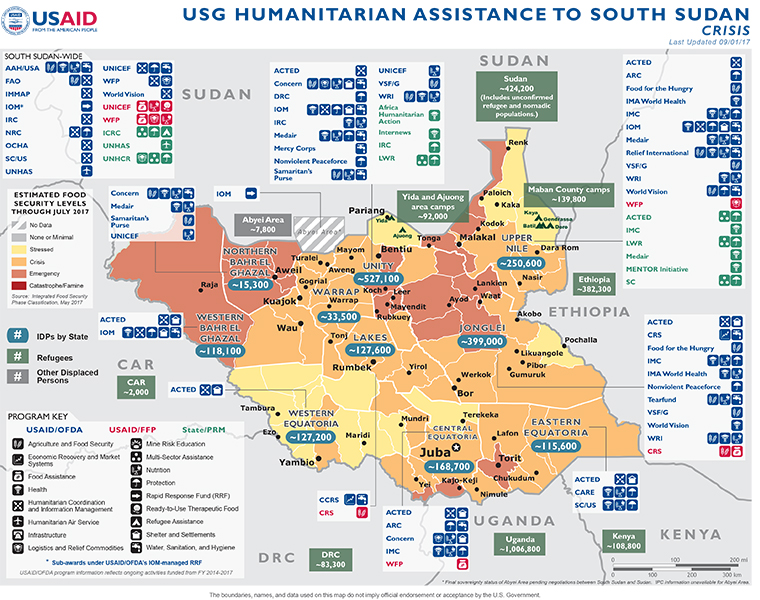
South Sudan Map - 09-01-2017 ![]() (pdf - 670k)
(pdf - 670k)
Numbers At A Glance
1.9 million
212,700
2 million
1 million
275,200
Humanitarian Funding
For the South Sudan Response
| USAID/OFDA | $129,252,395 |
| USAID/FFP | $336,608,368 |
| State/PRM | $52,810,000 |
Total USAID and State Emergency FY 2017 Funding for the South Sudan Crisis; Includes Funding for South Sudanese Refugees in Neighboring Countries: $728,685,903
Total USG Humanitarian Funding for the South Sudan Response in FY 2014-2017, Including Funding for South Sudanese Refugees in Neighboring Countires: $2,655,697,845
South Sudan Crisis Fact Sheet #11 - 09-01-2017 ![]() (pdf - 348k)
(pdf - 348k)
INSECURITY, DISPLACEMENT, AND HUMANITARIAN ACCESS
Relief actors reported nearly 630 humanitarian access incidents from January–July, including more than 130 humanitarian access incidents in South Sudan during the month of July alone, approximately 36 percent of which involved violence against humanitarian personnel, assets, or civilian infrastructure, the UN reports. In addition, at least 27 security incidents have forced approximately 300 relief workers to relocate from areas of operation to date in 2017.
The 130 access incidents in July, a 30 percent increase from the 100 incidents reported in June, represent the highest number recorded in a single month since 2016 and indicate increased looting, with 15 looting incidents reported across the country in July compared to six incidents in June. Six of the July incidents involved looting of commodity warehouses and humanitarian truck convoys in Eastern Equatoria, Lakes, Upper Nile, and Warrap states resulting in the loss of 670 metric tons (MT) of commodities. In addition to looting, humanitarian actors reported access denials by both Government of the Republic of South Sudan (GoRSS) and non-state armed actors in Central Equatoria State’s Kajo-Keji and Yei counties and Eastern Equatoria’s Torit County.
General insecurity and fighting between GoRSS-aligned and opposition forces in Upper Nile’s Maban and Maiwut counties have disrupted humanitarian operations and generated thousands of new internally displaced persons (IDPs). In Maiwut County, clashes resumed on July 27 in Maiwut town and surrounding areas near Pagak town, prompting people to temporarily flee to Ethiopia’s Gambella Region and the looting of humanitarian compounds in Maiwut and Pagak towns. According to international media, GoRSS troops captured Pagak, which hosts a key Sudan People’s Liberation Army-In Opposition (SPLA-IO) base, on August 7; local media report that SPLA-IO forces recaptured nearby Maiwut town on the same day, further fueling displacement.
Increased insecurity in the Maban area previously prompted humanitarian organizations to relocate staff to areas of relative safety in early July. On August 2, intercommunal clashes occurred at the Melut–Maban county border, prompting approximately 27 relief workers to relocate from Maban County’s Bunj town and temporarily disrupting some relief activities, including those serving refugee camps in the area. In response, humanitarian agencies coordinated with local staff to confirm population displacement figures and emergency relief needs related to the fighting and have since resumed reduced activities in the affected area. In mid-August, the number of South Sudanese refugees in Uganda reached 1 million; an average of 1,800 South Sudanese people arrived in Uganda per day in 2017, the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) reports. More than 85 percent of the refugees in Uganda were women and children, who cited forced conscription, sexual violence, and targeted killings by armed actors as primary reasons for fleeing.
From January–August 15, more than 180,000 South Sudanese refugees arrived in Sudan, surpassing estimates of 180,000 arrivals for all of 2017, UNHCR reports. More than 30 percent of the new arrivals settled in Sudan’s White Nile State, while relief actors also report a recent influx of refugees into Sudan’s South Darfur State. Since July, nearly 10,500 refugees have arrived in the state, citing escalating conflict and food insecurity in Western Bahr el Ghazal State, South Sudan, as primary reasons for fleeing. Humanitarian organizations estimate an additional 30,000–40,000 people will arrive in South Darfur by January 2018 and are developing contingency plans to address the influx. A total of 425,000 South Sudanese refugees were sheltering in Sudan as of September 1, according to UNHCR.
In addition to the refugees in Uganda and Sudan, more than 576,400 additional South Sudanese were sheltering in other neighboring countries, including the Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, and Kenya as of September 1. International donors have provided $303.5 million—or 22 percent—of the $1.4 billion required by UNHCR’s South Sudan Regional Refugee Response Plan, according to OCHA.
FOOD SECURITY AND NUTRITION
Countrywide food inflation rates in local currency had reached nearly 360 percent and staple food prices were increasing in most markets in South Sudan due to ongoing insecurity and road inaccessibility resulting from heavy rain as of late June, according to WFP. White sorghum prices increased between 9 and 20 percent from May to June in Lakes, Northern Bahr el Ghazal, Unity, and Upper Nile states, and white maize prices increased by 15 percent in Eastern Equatoria during the same period, WFP reports. The UN agency expects food prices to remain at elevated levels in the coming months, negatively affecting household food access.
Since January, USAID/FFP partner WFP has reached 4.2 million unique beneficiaries in South Sudan with general food distributions, food-for-assets assistance, and acute malnutrition prevention and treatment services, exceeding the total number assisted by the UN agency in all of 2016. Despite heavy and continual rainfall that has rendered many of the country’s roads impassable, WFP distributed approximately 28,400 MT of food commodities to 2.9 million people during July, representing the third consecutive month that WFP has surpassed the highest registered number of people assisted in the country since 2011. These beneficiaries included approximately 900,000 children younger than five years of age and 220,000 pregnant and lactating women.
In collaboration with other humanitarian organizations, WFP continues to reach vulnerable communities in more than 80 hard-to-reach areas in South Sudan through the integrated rapid response mechanism (IRRM), which features mobile teams of multi-sector technical specialists who assess and respond to the humanitarian situation. In July, approximately 1.7 million people in South Sudan received life-saving assistance through the IRRM.
Between July 28 and August 2, relief actors conducted a multi-sector interagency humanitarian assessment in Mvolo County, Western Equatoria State. Prior to late July, Mvolo was inaccessible due to ongoing insecurity; the rapid needs assessment marked the first time humanitarian agencies accessed the area since January. The assessment identified a lack of access to safe drinking water and acute levels of food insecurity due to increasing violence and widespread crop failure. According to the assessment team, local markets in the county were not functioning, and many families had depleted household food stocks and were surviving on wild fruit. During the assessment, the team screened more than 2,500 children younger than five years of age and 570 pregnant and lactating women for malnutrition, treating all those individuals diagnosed with severe and moderate acute malnutrition. In response to the assessment, USAID/FFP partner WFP has scaled up emergency food assistance operations in Mvolo, targeting 69,500 people through general food distributions.
USAID partner Catholic Relief Services (CRS) continues to support nutrition programming in Jonglei State’s Akobo, Bor, Duk, Pibor, and Twic East counties. Between April and June, CRS distributed more than 18 MT of High Energy Biscuits to approximately 2,400 pregnant and lactating women and 2,100 children younger than two years of age. During the same period, the non-governmental organization (NGO) trained more than 30 health workers on nutrition and community mobilization techniques and convened approximately 40 community meetings to review infant and young child feeding practices.
HEALTH AND WASH
Although the countrywide number of new weekly cholera cases is declining in South Sudan, cholera transmission remains active in 11 counties and health organizations continue to respond, according to the Health Cluster—the coordinating body for humanitarian health activities, comprising UN agencies, NGOs, and other stakeholders. Between June 18, 2016, and August 20, 2017, health actors recorded 19,850 suspected cholera cases and 355 related deaths across the country, representing a case fatality rate of 1.8 percent, exceeding the UN World Health Organization (WHO) emergency threshold of 1 percent.
In late July, the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF) supported vaccine management and transportation, social mobilization, and training activities in Eastern Equatoria’s Kapoeta East, Kapoeta North, Kapoeta South counties. UNICEF staff also supported cholera awareness campaigns via 20 radio stations in recent weeks, including broadcasting up to ten radio jingles per day with cholera messaging, and inserting cholera prevention messages into 27 talk shows and 24 interviews, reaching approximately 1.8 million people. Through GoRSS Ministry of Health and partners, UNICEF is raising public awareness on cholera in UN Mission in the Republic of South Sudan (UNMISS) protection of civilian (PoC) sites and IDP settlements through street announcements, traditional performances, and drama shows.
In mid-August, humanitarian agencies completed an oral cholera vaccination (OCV) campaign, reaching more than 350,000 people in four priority counties. The American Refugee Committee (ARC)—with support from the USAID/OFDA-funded, International Organization for Migration (IOM)-managed Rapid Response Fund (RRF)—conducted the campaign in Kapoeta East, reaching approximately 66,000 people. In Kapoeta South, health workers vaccinated nearly 78,500 people, or more than 50 percent of the county’s population. In addition to the OCV campaign, relief actors recently rehabilitated or repaired nearly 100 boreholes in Kapoeta East, Kapoeta North, and Kapoeta South, improving access to safe drinking water for more than 48,500 people. Humanitarian staff also delivered buckets, soap, and water purification tablets to nearly 2,000 households and reached more than 1,600 individuals with hygiene promotion messaging in the three counties.
During the month of July, UNICEF conducted five mobile health response missions in Central Equatoria, Jonglei, and Unity. During the missions, the UN agency vaccinated approximately 19,700 children against measles and 27,400 children against polio, and provided clean delivery kits to 860 pregnant women. In addition, UNICEF conducted 10,200 primary health care consultations. Health actors recorded more than 1.2 million malaria cases in South Sudan from January–July, according to the UN. Both cholera and malaria are endemic to South Sudan and typically increase during the May-to-September rainy season.
To improve water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) conditions in Jonglei, USAID partner CRS recently rehabilitated more than 20 boreholes, expanding access to safe drinking water for nearly 20,300 people in Bor, Duk, and Pibor between April and June. CRS also trained approximately 180 promoters on basic health and hygiene tools and disseminated safe hygiene and sanitation messaging to more than 32,500 individuals in Bor, Duk, Pibor, and Twic East via commodity distributions, community meetings, and house-to-house visits.
PROTECTION
A protection NGO participated in the July 28–August 2 multi-sector interagency humanitarian assessment in Mvolo and identified significant protection concerns, including attacks by unknown armed actors and cattle raiding. The protection assessment, which consisted of 10 focus group discussions with 100 participants, indicated the greatest fear among women was abduction and rape, and that women face constant harassment while fetching firewood or water. The NGO noted low reporting of gender-based violence (GBV) cases, likely due to stigma associated with the topic. Assessed populations also identified child labor and early and forced marriage as prevalent protection concerns, which are not uncommon in conflict-affected areas of South Sudan. In response to issues identified, the organization recommends creating more child-friendly spaces, raising awareness of GBV, and creating and strengthening early-warning and early-response systems. The organization also plans to promote the participation of women in governance and decision-making structures in Mvolo.
With USAID/OFDA support, the same NGO also conducted an August protection assessment in Unity’s Mayom town comprised of nine key informant interviews and three focus group discussions with more than 75 participants. Discussion group participants indicated that the presence of armed cattle raiders in nearby towns exacerbated perceptions of insecurity and created the potential for violence due to competition for resources, as Mayom’s population consists primarily of cattle herders. In addition, participants reported GBV—including domestic violence, sexual assault, and rape—and forced recruitment of youth into armed groups as dominant concerns. In response, the NGO assessment team conducted a one-day child protection training with 20 participants, comprising local community leaders, teachers, school representatives, and women’s group members. Longer-term response strategies include working with protection actors to conduct advocacy activities to deter local military actors from further recruitment of youth. The NGO recommends that protection and health actors engage in GBV awareness-raising activities, including the dissemination of access protocols to vital services such as post-exposure prophylaxis and psychosocial services, and that a stronger visible presence of UNMISS forces and a more proactive approach by local police could deter GBV incidents.
OTHER HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE
On August 23, Government of Israel Ambassador to South Sudan Hanan Goder and Israeli humanitarian NGO staff distributed more than 5 MT of food assistance to vulnerable populations in the capital city of Juba, international media report. The food assistance contribution was coordinated by the Government of Israel Agency for International Development Cooperation and the Israeli embassy in Juba.
On August 24, the Government of Japan (GoJ) contributed $10 million in emergency response assistance for South Sudanese refugees and host communities in Uganda, according to a joint UN agency press release. The funding—channeled through UNHCR, UNICEF, and WFP—will help provide relief items such as blankets, kitchen sets, and mattresses; improve community infrastructure; provide access to safe drinking water and immunizations for more than 160,000 people; and purchase nearly 4,600 MT of food commodities to feed approximately 1 million refugees. GoJ Minister of Foreign Affairs Nobuo Kishi made the funding pledge during the June 23 Solidarity Summit to address humanitarian funding needs for the refugee response in Uganda.
CONTEXT
The January 2005 signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) between the Government of Sudan and the southern-based Sudan People’s Liberation Army (SPLA) officially ended more than two decades of north–south conflict during which famine, fighting, and disease killed an estimated 2 million people and displaced at least 4.5 million others within Sudan.
The GoRSS declared independence on July 9, 2011, after a referendum on self-determination stipulated in the CPA. Upon independence, USAID designated a new mission in the capital city of Juba.
On December 15, 2013, clashes erupted in Juba between factions within the GoRSS and quickly spread into a protracted national conflict with Jonglei, Unity, and Upper Nile states representing the primary areas of fighting and displacement. On December 20, 2013, USAID activated a USAID Disaster Assistance Response Team (DART) to lead the USG response to the developing crisis in South Sudan. USAID also stood up a Washington, D.C.-based Response Management Team (RMT) to support the DART.
On August 26, 2015, GoRSS President Salva Kiir Mayardit signed a peace agreement that the Sudan People’s Liberation Army-In Opposition (SPLA-IO) and other stakeholders had signed on August 17. Opposition leader Riek Machar returned to Juba and was sworn in as FVP on April 26, 2016; GoRSS President Salva Kiir Mayardit appointed a Transitional Government of National Unity on April 28, 2016.
Fighting between SPLA and SPLA-IO forces broke out in Juba on July 7, 2016, displacing thousands of people and prompting FVP Machar to flee. As a result, the U.S. Embassy in Juba ordered the departure of non-critical USG personnel from South Sudan on July 10. Although ongoing heightened tensions persist in the country and the humanitarian situation remains precarious, the U.S. Department of State ended the ordered departure status for the U.S. Embassy in Juba on January 5, 2017.
Insecurity, landmines, and limited transportation and communication infrastructure restrict humanitarian activities across South Sudan, hindering the delivery of critical assistance to populations in need.
On October 14, 2016, U.S. Ambassador Mary Catherine Phee redeclared a disaster in South Sudan for FY 2017 due to the humanitarian crisis caused by ongoing violent conflict, resultant displacement, restricted humanitarian access, and the disruption of trade, markets, and cultivation activities, which have significantly increased food insecurity and humanitarian needs.
On February 20, the IPC Technical Working Group declared Famine levels of food insecurity in Leer and Mayendit. On June 21, the IPC Technical Working Group declared that sustained humanitarian interventions have moderately improved food security conditions in Unity’s Leer and Mayendit counties, resulting in the removal of the Famine level designation for acute food insecurity in the counties. However, life-threatening food insecurity continues to impact households across South Sudan, particularly in conflict-affected areas.







Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.